Breast health is of paramount importance for every woman. In cases where abnormalities are detected, a breast biopsy becomes a crucial diagnostic tool. This article provides a comprehensive guide to understanding breast biopsies, their types, procedures, and significance in breast health management.
Introduction
A breast biopsy is a vital diagnostic procedure that aids in identifying abnormalities within breast tissue. This article sheds light on the various aspects of breast biopsies, their importance, types, procedures, and post-biopsy care.
What is a Breast Biopsy?
A breast biopsy is a medical procedure wherein a small sample of breast tissue is extracted for microscopic examination. This examination helps determine whether a lump or abnormality in the breast is cancerous or non-cancerous.
Reasons for a Breast Biopsy
Breast biopsies are typically recommended when mammograms, ultrasounds, or clinical exams reveal unusual changes in breast tissue. These changes could include palpable lumps, architectural distortion, or suspicious calcifications.
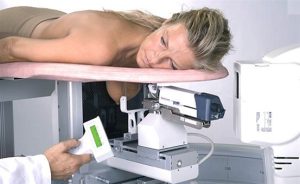
Types of Breast Biopsies
- Fine-Needle Aspiration Biopsy (FNAB)
FNAB involves using a thin needle to extract fluid or cells from the breast lump. This method is often employed for cystic lumps or masses.
- Core Needle Biopsy (CNB)
CNB employs a larger needle to extract small cylinders of tissue. It provides a more accurate diagnosis of non-palpable lesions and microcalcifications.
- Vacuum-Assisted Biopsy (VAB)
VAB employs vacuum pressure to obtain multiple tissue samples through a single needle insertion. It’s useful for larger lesions and provides comprehensive sampling.
- Excisional Biopsy
This surgical procedure involves removing the entire lump or a portion of suspicious tissue for examination. It’s usually recommended when other methods are inconclusive.
When is a Breast Biopsy Recommended?
A breast biopsy is recommended when imaging tests indicate potential malignancy or when a lump is palpable. Early detection through biopsies plays a pivotal role in effective treatment.
- How to Prepare for a Breast Biopsy
Before the procedure, inform your doctor about medications, allergies, and medical conditions. Avoid blood-thinning medications and discuss any concerns you may have.
- The Breast Biopsy Procedure
The biopsy procedure involves local anesthesia to minimize discomfort. Depending on the type of biopsy, a small incision may be made, or a needle inserted to extract tissue samples.
- Understanding Biopsy Results
Pathologists analyze tissue samples for cancerous cells. Results are categorized as benign, atypical, or malignant. Further tests might be recommended for a conclusive diagnosis.
- Potential Complications and Risks
While breast biopsies are generally safe, risks include bleeding, infection, and scarring. These complications are rare and usually manageable with proper care.
- Follow-Up Care After a Biopsy
Post-biopsy care involves rest, avoiding strenuous activities, and keeping the biopsy site clean. Follow medical instructions diligently for a smooth recovery.
- Breast Biopsy Myths Debunked
Dispelling misconceptions surrounding breast biopsies promotes informed decision-making and empowers individuals to prioritize their breast health.
- Importance of Regular Breast Screenings
Regular mammograms and screenings enhance the chances of early detection, making treatment more effective and improving outcomes.
- Empowerment through Knowledge
Understanding breast biopsies empowers individuals to proactively engage in their healthcare journey, fostering a sense of control and informed decision-making.
- Supporting Breast Health Awareness
Breast health awareness campaigns play a vital role in educating individuals about the significance of screenings, biopsies, and overall breast health.
Conclusion
Breast biopsies are a critical tool in the diagnosis of breast abnormalities. Early detection through regular screenings and timely biopsies can significantly impact treatment outcomes and save lives. Prioritizing breast health empowers individuals to take charge of their well-being and make informed choices.
FAQs
Q1: Are breast biopsies painful? A: Most biopsies involve only mild discomfort due to local anesthesia. Discomfort is usually manageable and short-lived.
Q2: Can I resume regular activities after a biopsy? A: Depending on the type of biopsy, your doctor will provide specific instructions. Generally, strenuous activities should be avoided for a few days.
Q3: Is a surgical biopsy more accurate than other methods? A: Surgical biopsies provide a more extensive tissue sample, often leading to a more accurate diagnosis. However, less invasive methods are also highly reliable.
Q4: Can I drive myself home after a biopsy? A: If local anesthesia is used, you should be able to drive yourself home after the procedure. However, it’s best to have someone accompany you if possible.
Q5: How often should I undergo breast screenings? A: Consult your healthcare provider for personalized recommendations. In general, mammograms are recommended annually for women over 40.


 Home
Home