Nicotinamide adenine dinucleotide (NAD+) therapy has gained attention in the wellness and anti-aging realms for its potential to enhance cellular function and promote overall health. This therapy, centered around a coenzyme found in all living cells, offers a promising avenue for optimizing various physiological processes and supporting well-being.
Table of Contents
Understanding NAD+
NAD+ is a crucial coenzyme that plays a central role in cellular metabolism. It acts as a vital component in energy production, DNA repair, and the regulation of various cellular functions. However, NAD+ levels tend to decline with age, potentially contributing to various age-related conditions and diminishing overall health.
NAD+ Therapy Explained
NAD+ therapy involves the administration of NAD+ precursors or direct NAD+ supplementation to elevate cellular levels of this coenzyme. Precursors like nicotinamide riboside (NR) or nicotinamide mononucleotide (NMN) are converted into NAD+ in the body, augmenting cellular stores and potentially supporting numerous biological processes.
Potential Benefits of NAD+ Therapy
Energy Metabolism: NAD+ is integral to mitochondrial function, enhancing energy production in cells. Elevating NAD+ levels may potentially improve cellular energy metabolism and overall vitality.
DNA Repair: NAD+ plays a role in DNA repair mechanisms, potentially aiding in maintaining genomic stability and countering cellular damage caused by aging or environmental factors.
Cellular Health: Higher NAD+ levels are associated with improved cellular function, which may positively impact various systems in the body, including neurological, cardiovascular, and metabolic functions.
Anti-Aging Properties: While not a fountain of youth, NAD+ therapy is being studied for its potential to support healthy aging by addressing age-related declines in cellular function.
Neuroprotective Effects: Some research suggests that NAD+ may support brain health and cognitive function, potentially offering neuroprotective benefits against age-related cognitive decline.
NAD+ Therapy Administration
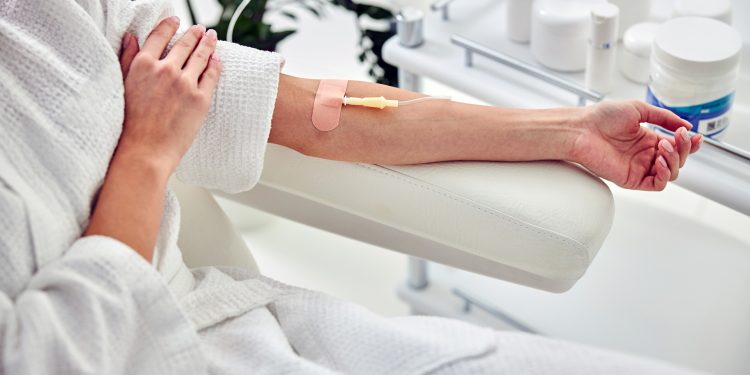
NAD+ therapy can be administered intravenously (IV), orally through supplements, or via nasal sprays. IV therapy delivers NAD+ directly into the bloodstream, allowing for quick absorption and potentially more immediate effects, while oral supplementation may take longer to elevate NAD+ levels systemically.
NAD+ IV therapy is administered by infusing NAD+ directly into the bloodstream. This method ensures rapid and efficient absorption of this coenzyme, providing numerous potential health benefits, from enhanced energy levels to improved cellular function. The intravenous delivery of NAD+ is a popular approach for those seeking to optimize their wellness and vitality.
Considerations and Caution
While NAD+ therapy shows promise, its long-term effects and safety in humans require further research. Additionally, individual responses to NAD+ therapy may vary, and its use should be approached with caution, especially for individuals with underlying health conditions or those taking medications.
Potential Side Effects
Limited data suggests that NAD+ therapy is generally well-tolerated, but some individuals may experience side effects such as nausea, fatigue, headaches, or gastrointestinal disturbances. Consulting a healthcare professional before starting NAD+ therapy is recommended, especially for those with existing health concerns.
NAD+ therapy holds promise as a potential tool for optimizing cellular function, supporting various physiological processes, and potentially promoting overall wellness. While research into its efficacy and safety continues, its use in clinical settings and wellness practices is evolving. As with any emerging therapy, consulting healthcare professionals knowledgeable about NAD+ therapy and its implications is crucial for individuals considering its use.
Understanding the multifaceted nature of NAD+ and its pivotal role in cellular metabolism, scientists and healthcare practitioners are exploring its potential applications beyond conventional wellness practices. This coenzyme’s impact on cellular health presents a fascinating avenue for future research into combating age-related declines and optimizing overall health.
Conclusion
NAD+ therapy holds promise as a potential tool for optimizing cellular function, supporting various physiological processes, and potentially promoting overall wellness. While research into its efficacy and safety continues, its use in clinical settings and wellness practices is evolving. As with any emerging therapy, consulting healthcare professionals knowledgeable about NAD+ therapy and its implications is crucial for individuals considering its use. By unlocking the potential of NAD+ in cellular health, this therapy represents a fascinating frontier in the quest for improved well-being and healthier aging.


 Home
Home