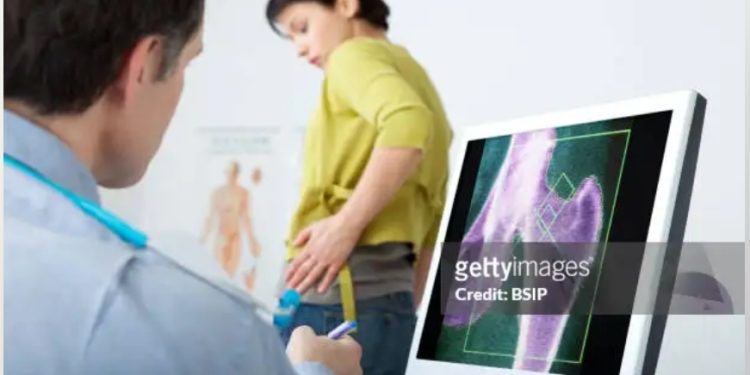
In healthcare, the quest for advanced diagnostic tools never ceases. DEXA (Dual-Energy X-ray Absorptiometry) scans have become valuable when assessing bone health and diagnosing bone diseases. However, like any medical technology, Dexa Scan has benefits and limitations. This blog will look at both, shedding light on this critical tool that helps keep our bones strong and healthy.
The Benefits of DEXA X-ray in Diagnosing Bone Diseases
- Exceptional Precision
One of the standout advantages of DEXA X-ray is its remarkable precision. This imaging technique can measure bone density with incredible accuracy, providing detailed information about the state of your bones. It allows healthcare providers to detect even subtle changes in bone density, which can be crucial for early diagnosis and intervention.
- Low Radiation Exposure
While we often associate X-rays with radiation exposure, DEXA scans use less radiation than traditional X-ray imaging. The low dose of radiation used in DEXA scans makes it a safe option for frequent bone density monitoring, even for vulnerable populations such as the elderly.
- Quick and Non-Invasive
DEXA X-ray scans are quick and non-invasive, making them well-tolerated by patients. The procedure typically involves lying on an examination table for a short period. No injections or contrast agents are needed, making it a hassle-free experience.
- Versatile Applications
DEXA scans are versatile and can diagnose many bone diseases, including osteoporosis, osteopenia, and metabolic disorders. They are also valuable in assessing the effects of certain medications on bone health and monitoring treatment progress.
- Effective Screening Tool
DEXA scans are practical screening tools for assessing bone health, especially in populations at risk for osteoporosis or fractures. They help identify individuals who may benefit from preventive measures or early intervention, reducing the risk of debilitating fractures later in life.
- Long-Term Monitoring
DEXA X-ray is not limited to diagnosis; it is also instrumental in long-term monitoring. Patients with conditions like osteoporosis or those undergoing treatment can have regular DEXA scans to track changes in bone density over time. This flexibility allows healthcare providers to assess the effectiveness of interventions and adjust treatment plans accordingly.
- Comparative Data
DEXA scans provide baseline data for bone density, which can be compared with future scans. This longitudinal data helps identify trends and changes in bone health, guiding healthcare decisions and interventions for better patient care.
- Predictive Tool for Fracture Risk
DEXA scans diagnose bone diseases and serve as predictive tools for fracture risk. By assessing bone density, healthcare providers can estimate an individual’s likelihood of experiencing bone fractures. This information is invaluable for making informed decisions about preventive measures and treatment options.
The Limitations of DEXA X-ray in Diagnosing Bone Diseases
- Limited Information on Bone Quality
While DEXA X-ray excels at measuring bone density, it provides limited information about bone quality. Bone quality involves factors like bone microarchitecture, which can also impact bone strength. Some other imaging techniques, like high-resolution CT scans, may provide more insights into bone quality.
- Unable to Detect All Bone Diseases
DEXA scans are primarily designed to assess bone mineral density, which makes them excellent for diagnosing conditions like osteoporosis. However, they may not be the best choice for detecting certain rare bone diseases or bone infections. In such cases, additional imaging methods or tests may be necessary.
- Results Interpretation Challenges
Interpreting DEXA scan results requires expertise, and different healthcare providers can vary how results are analyzed. It’s crucial to consult with a specialist experienced in reading DEXA scans to ensure accurate diagnosis and treatment planning.
- Limited Use in Monitoring Soft Tissues
DEXA X-ray is primarily focused on bone assessment. It may not provide detailed information about soft tissues or surrounding structures. In cases where both bone and soft tissue evaluation is required, other imaging modalities such as MRI or ultrasound may be necessary.
- Age and Size Limitations
DEXA scans may be less accurate in specific populations, such as children, due to their rapid bone growth or individuals with obesity. The technique may not provide reliable results for those with unusual bone shapes or sizes, leading to potential inaccuracies in diagnosis.
- Cost and Accessibility
While DEXA scans are widely available, they may not be accessible to everyone due to cost or location. Insurance coverage and geographic availability can affect an individual’s access to this diagnostic tool.
- Does Not Replace Clinical Evaluation
It’s important to emphasize that DEXA X-ray is just one comprehensive bone health assessment component. Clinical evaluation, medical history, and risk factors are crucial in diagnosing bone diseases. A holistic approach ensures a more accurate and complete understanding of a patient’s bone health.
- Not Suitable for All Ages
DEXA scans are typically recommended for adults aged 50 and older or those with specific risk factors for bone diseases. Alternative imaging methods may be more appropriate for diagnosing bone-related issues in younger individuals or children.
Final Thoughts:
In conclusion, the DEXA scan is a valuable tool in diagnosing bone diseases, offering precision, safety, and convenience. However, it’s essential to recognize its limitations and understand that it may not be suitable for all bone-related conditions or assessing bone quality. Look for an “X-ray near me” to determine the most appropriate diagnostic approach based on your needs and medical history. We can anticipate further bone disease diagnosis and management improvements as technology advances.


 Home
Home