Is Brain Stroke Curable? Your Guide to Stroke Treatment in Bangalore
Today, we’re on a quest to answer a big question: Can a person recover from a brain stroke? Picture it like unclogging a traffic jam in your brain – and we’re about to spill the beans on how it’s done. This is your guide to stroke treatment in Bangalore.
So, here’s the deal: your brain is on a busy highway, and a stroke throws in a major speed bump. It messes with how your body moves, thinks, and talks. But, hold on, can we do something about it?
That’s what we’re here to find out.
In this blog, we will dive into the treatment methods and address some common questions about stroke recovery:
- Can you recover from a brain stroke?
- How likely are you to survive a brain stroke?
- Is it possible to fully bounce back?
- What treatments are available for strokes?
But first, let’s answer a few basic questions.
What is a Brain Stroke?
Often referred to as a “brain attack,” a brain stroke occurs when blood flow to the brain is disrupted or stopped.
The brain, like any powerhouse, requires a constant supply of oxygen and nutrients to function optimally. When this supply is interrupted, even briefly, it can result in significant problems.
Brain cells start to perish within minutes without oxygen or blood, leading to a loss of vital functions.
A stroke can affect various aspects of life, including your ability to:
- Speak
- Move
- Eat
- Think
- Remember (memory)
- Control your emotions
- Control your bowel and bladder
What Causes a Brain Stroke?
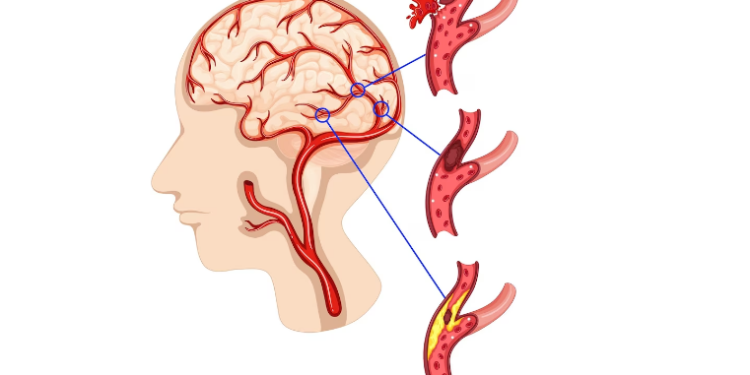
There are two primary types of strokes: ischemic and hemorrhagic.
1. Ischemic Stroke: This is the most common type, occurring when a major brain blood vessel is blocked. The blockage can be due to a blood clot or a buildup of fatty deposits, known as plaque.
2. Hemorrhagic Stroke: This type happens when a blood vessel in the brain ruptures, causing blood to spill into nearby tissues. The increased pressure in the brain tissue can lead to further damage.
What Are the Risk Factors for a Brain Stroke?
Understanding the risk factors for stroke is crucial. While some factors can be changed or managed, others are beyond our control. Let’s take a look:
1. Changeable Risk Factors:
- High Blood Pressure
- Heart Disease
- Diabetes
- Smoking
- Birth Control Pill Use
- History of Transient Ischemic Attacks (TIAs)
- High Red Blood Cell Count
- High Blood Cholesterol and Lipids
- Lack of Exercise
- Obesity
- Excessive Alcohol Use
- Illegal Drug Use
- Abnormal Heart Rhythm
- Cardiac Structural Abnormalities
2. Unchangeable Risk Factors:
- Older Age
- Race
- Gender
- History of Prior Stroke
- Heredity or Genetics
Recognizing Stroke Symptoms- What Are the Warning Signs?
A stroke is an emergency, and recognizing its symptoms is crucial for prompt intervention. Remember FAST:
- F – Face Drooping: One side of the face droops or feels numb.
- A – Arm Weakness: One arm is weak or numb.
- S – Speech Difficulty: Slurred speech or difficulty speaking.
- T – Time to Call 911: If any of these signs appear, call for help immediately. Note the time the symptoms began.
Your Guide to Stroke Recovery and Treatment
Alright, so now that we know what a brain stroke is and what causes it, let’s talk about the nitty-gritty of dealing with it. Can you recover from a brain stroke? How likely are you to survive, and is there a chance to fully bounce back? What treatments are available to get you back on your feet?
How Is a Brain Stroke Treated? Is it Curable?
So, the million-dollar question – can we actually cure a stroke? Well, the short answer is that while it’s not considered curable, there’s a lot we can do to improve symptoms and functional abilities.
Treatments for strokes usually involve a mix of medications, therapy, and lifestyle adjustments.
Your doctor will tailor the treatment plan based on a few key things:
- Your age, overall health, and past health
- The type and severity of the stroke
- The location in your brain where the stroke happened
- What caused the stroke in the first place
- How well you handle certain medicines, treatments, or therapies
What Are the Emergency Treatment Methods for a Brain Stroke?
Prompt medical evaluation and treatment are imperative for stroke recovery. Immediate actions include:
- Clot-busting medicines (thrombolytics or fibrinolytics): Administered within 3 hours of an ischemic stroke, these medicines dissolve blood clots, minimizing damage to brain cells.
- Medicines and therapy to reduce or control brain swelling: Intravenous fluids play a crucial role in managing brain swelling, particularly after a hemorrhagic stroke.
- Neuroprotective medicines: These medications shield the brain from damage and oxygen deprivation.
- Life support measures: Utilizing a ventilator for breathing support, intravenous fluids, proper nutrition, and blood pressure control are integral life support measures.
- Craniotomy: A surgical procedure that addresses issues like removing blood clots, relieving pressure, or repairing bleeding in the brain.
- Mechanical Thrombectomy: Involves catheter-based clot removal, effective within 6 to 24 hours after an ischemic stroke.
- Stents and Surgery: Stents support weakened artery walls; surgery may remove clots and plaques if other treatments fail.
- Medications for Hemorrhagic Stroke: Medicines to counteract blood thinners, control blood pressure, prevent seizures, and restrict blood vessel constriction.
How does the timing of treatment impact its effectiveness?
Treatment is most effective when initiated promptly. The urgency is particularly crucial for clot-busting medicines, which must be administered within a 3-hour window after an ischemic stroke.
Early intervention helps minimize the extent of brain damage and improves overall outcomes.
Recovery: Life After a Brain Stroke?
Life after a stroke depends on the extent of brain damage.
Many people face challenges with mobility, speech, and daily activities.
Recovery time varies for each person, taking weeks, months, or even years. Some fully recover, while others face long-term disabilities.
Recovery after a brain stroke focuses on getting back as much function as possible and preventing future strokes. You may need therapy and assistance at home.
Stroke recovery begins early, typically focusing on four main areas:
- Speech Therapy: Helps relearn speech or explore alternative communication methods.
- Cognitive Therapy: Addresses changes in thinking, reasoning, and emotional responses.
- Relearning Sensory Skills: Assists in adjusting to altered sensations caused by the stroke.
- Physical Therapy: Focuses on regaining muscle strength, and balance, and adapting to limitations.
Rehabilitation may occur in various settings, aiming for optimal recovery and improved quality of life.
How to Deal with a Brain Stroke?
Strokes are emergencies. Quick treatment can save lives. Call for help at the first sign of a stroke.
You should be in the hospital within three hours. Tests will be done to check for problems, and if it’s a clot, you’ll get medicine to dissolve it. Treatment depends on how bad the stroke is. You may stay in the hospital for a few days and need medication, maybe surgery.
How to Prevent Another Stroke?
You may need medication to prevent future strokes. Eating healthy and managing conditions like diabetes and high blood pressure are crucial.
In short, while strokes may not be curable, quick treatment and rehab can help you get better. After a stroke, therapy and support are vital for recovery and preventing more strokes.
How Many Strokes Can Someone Survive?
There isn’t a clear-cut answer to how many strokes a person can survive. However, the more strokes someone experiences, the greater the risk of brain damage, impacting their chances of survival.
Additionally, timely medical intervention is a crucial factor influencing the overall likelihood of surviving a stroke.
Understanding the Impact of Multiple Strokes on Life
When someone goes through more than one stroke, it not only affects their health but also increases the chances of facing another stroke and lowers their odds of survival.
A study in 2022 looked at over 300,000 people in Australia and New Zealand, around 73 years old on average, showing how survival rates change over time after the first stroke:
| Time after First Stroke | Survival Chance | Chance of Another Stroke |
| 3 months | 79.4% | 7.8% |
| 1 year | 73% | 11% |
| 5 years | 52.8% | 19.8% |
| 10 years | 36.4% | 26.8% |
People who’ve had a small stroke, called a ministroke or TIA, face different risks. A study in 2016 found these chances of having a stroke after a TIA:
- 1.5% within 2 days
- 2.1% within 7 days
- 2.8% within 30 days
- 5.1% within 1 year
Generally, around one in four people who’ve had a stroke will experience another one.
While there isn’t a specific number of strokes that are considered fatal, having more strokes increases the risk of lasting damage or death.
But here’s some good news: up to 80% of strokes could be prevented. If you’re worried about having multiple strokes, talking to a doctor can help figure out ways to lower the risk and keep you healthy.
Key Takeaways
- A stroke is a medical emergency.
- It can be caused by various factors, both changeable and unchangeable.
- Prompt recognition of symptoms and seeking immediate medical help increase the chances of recovery.
- While not all strokes can be prevented, lifestyle changes and medications significantly reduce risks.
- Life after a stroke varies, and rehabilitation is essential for improvement.
- If you experience symptoms resembling a stroke, even if they are brief, seek medical attention promptly.
A Final Thought
In essence, understanding strokes empowers us to take proactive steps in prevention, recognize warning signs, and support those on their journey to recovery.
If you have concerns or questions about brain strokes, contact us – Best neurology hospitals in bangalore healthcare.
From medical procedures to supportive rehabilitation, our comprehensive approach addresses immediate concerns and long-term effects in stroke and paralysis treatment.
So, empower yourself by taking proactive steps towards your healthcare.
Your journey to the best stroke treatment in Bangalore begins with a simple step – consultation.


 Home
Home