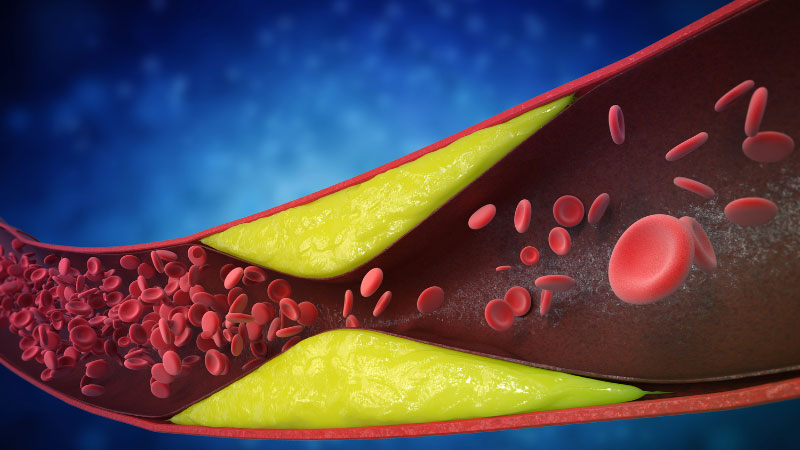
Atrial fibrillation (AF or Afib) is characterized as an irregular and chaotic beating of the heart’s upper chambers. AFib increases the risk of blood clots in the heart. These clots make people more likely to experience heart problems like heart failure and stroke. AFib is the primary diagnosis in more than 454,000 hospital admissions in the United States annually, according to the CDC (Centre for Disease Control and Prevention).
Atrial fibrillation ablation is a medical procedure that treats atrial fibrillation. This blog will look into the relationship between Afib and blood clot formation. We will also learn the risk factors of Afib and prevention techniques to reduce these risks. Additionally, medication like Eliquis 2.5 mg tablet helps to lower the risk of Afib by reducing blood clotting.
What Is Atrial Fibrillation Ablation?
Ablation is the surgical procedure to treat atrial fibrillation. It uses radiofrequency energy and cryoablation to break up the electrical signals that result in Afib and maintain a regular heart rhythm. It is performed to restore normal cardiac rhythm.
If you have Afib symptoms, such as a rapid, fluttering heartbeat, and they haven’t subsided despite medication or other therapies, your doctor may advise this kind of ablation.
Relation Between Afib & Blood Clot Formation
Blood clots are jelly clumps of blood cells that form in the veins and arteries. The purpose of blood clots is to stop bleeding. It can cause severe health conditions such as:
DVT (Deep Vein Thrombosis): Deep vein thrombosis, or DVT, happens when a thrombus or blood clot is present in one or more deep veins, usually in the legs. This disorder causes pain or inflammation in legs. Those with Afib are at high risk of DVT due to blood clot formation.
Pulmonary Embolism: A blood clot that stops blood flow to an artery in the lung is called a pulmonary embolism. A blood clot usually starts in a deep vein in the leg and moves to the lung. Sometimes the clot forms in a vein in another part of the body. Deep vein thrombosis (DVT) is when a blood clot forms in one or more of the body’s deep veins.
Heart Attack (Stroke): A heart attack or stroke occurs when the blood flow to the heart is cut off or slowed. Most of the time, the blockage is caused by blood clots. Hence, the people with Afib are more likely to get a stroke or heart attack. In the USA every 40 seconds someone has a stroke or heart attack, reported by the CDC (Centre for Disease Control and Prevention).
Cerebral Venous Thrombosis (CVT): If you have AFib, these clots are likely to travel to your brain. The effects of a blood clot in the brain may be severe. Brain arteries or veins may develop blood clots. Therefore it’s crucial to be aware of the symptoms of blood clots and Afib.
There is a deep relation between blood clot development and atrial fibrillation. You risk developing blood clots in the upper chambers of your heart if you have atrial fibrillation.
Risk Factors of Afib and Blood Clots
Various factors increase the risk of getting blood clots and atrial fibrillation. Here are the most prevalent risks of Afib and blood clots:
- Age: As you age, your chance of getting AFib goes up. It is estimated that 0.3% of people with Afib are 40 years old and 5%–9% are 60–80. About 10% are over 80 years old, as per the National Library of Medicine (NLM).
- Smoking and Alcohol: Nicotine is a chemical in tobacco you smoke. It can make your heart beat faster. It further leads to arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) and atrial fibrillation. Drinking alcohol affects the electrical signals of your heart and leads to Afib.
- Family History or Genetics: Genetic mutation (changes in the structure of genes) or a family history increase the risks of Afib.
- Heart surgery or heart disorders: if you have heart diseases that were there when you were born, you are at a high risk of getting Afib. People who have had a heart attack or surgery on their heart are also more likely to get the condition.
- Thyroid: If the thyroid is overactive (hyperthyroidism), it directly affects your heart and leads to arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat). It also results in tachycardia (fast heartbeat) and heart palpitations.
Prevention Strategies for Afib and Blood Clots
Afib and blood clots can cause severe health concerns. It is crucial to take preventive steps to reduce the risks of these conditions. Maintaining a healthy lifestyle and medication can help reduce those risks.
A Healthy Lifestyle
Choosing a healthy way of life can help you avoid AFib, other types of heart disease, and blood clots. A healthy diet and regular physical activities can lower your chances of developing blood clots and Afib. Here are few tips:
- Do things like walking, running, biking, and swimming daily.
- Eat a diet that is well-balanced and low in salt, saturated fats (unhealthy fats), and cholesterol.
- Limit the coffee and alcohol you drink.
- Don’t smoke.
Atrial Fibrillation Ablation
Doctors use different types of ablation procedures to minimize the risk of Afib. Here are some of the significant Afib Ablation:
- Surgical ablation: A surgical ablation is an open-heart ablation; a standard procedure cardiac surgeons use to treat Afib. These days, scarring your heart with heat or freezing waves is also used to stop the arrhythmia (irregular heartbeat) causing electrical signals.
- Catheter ablation: It is also called radiofrequency ablation due to the use of radiofrequency in this process. Radiofrequency are heat waves similar to microwave heat used to burn the small area of the heart that causes Afib. These waves destroy the abnormal tissue without harming the rest of the heart tissues.
- Cryoablation: It involves disabling the heart cells that cause Afib. A tiny flexible tube known as a balloon catheter is used to find and freeze the cells responsible for irregular heartbeats. Doctors use the advanced imaging technology to guide the catheter to disable the abnormal heart cells.
Medications
If you have AFib, your doctor might give you blood thinners to lower the chance that your blood will clot. They may also give you other medicines that follow atrial fibrillation guidelines to help restore your heartbeat and pulse. Medication such as Eliquis 2.5 mg tablet treats Afib effectively, is available at the best Canadian online pharmacy.
Conclusion
In conclusion, Atrial fibrillation (AFib) is a heart disease that causes the heart to beat in a way that isn’t regular. This increases the chances that a blood clot will form in the heart. These blood clots can cause significant health problems like heart failure and stroke. Atrial fibrillation ablation is a surgery that interrupts abnormal electrical messages to get the heart back to a normal rhythm.
AFib and blood clots are more likely to happen if you are older, smoke, drink alcohol, have a history of heart problems in your family, and take certain medicines. Risks of AFib and blood clots can be reduced by taking preventive steps, like living a healthy lifestyle and taking medications as recommended.


 Home
Home