What is Thermogenesis?
Thermogenesis is the process of heat production in your body. It happens when your body breaks down food, contracts muscles, and activates specialized tissues like brown adipose tissue (BAT). The heat produced by thermogenesis helps to keep your body warm and functioning properly.
There are a few things you can do to increase your thermogenesis and burn more calories, such as eating protein-rich foods, adding spice to your meals, getting regular exercise, and spending time in the cold. Increasing your thermogenesis can help you lose weight.
The amount of heat your body produces is measured in calories. The more thermogenesis you have, the more calories you will burn. This is why some people can eat more than others without gaining weight.
However, it’s important to note that individual calorie needs depend on factors such as age, sex, activity level, and body composition. Therefore, it’s always advisable to monitor your calorie intake and energy expenditure with TDEE Calculator to achieve your weight loss goals.
Types of Thermogenesis
Depending on whether or not they are initiated through locomotion and intentional movement of the muscles, thermogenic processes can be classified as one of the following:
| Type of Thermogenesis | Cause | Contribution to Heat Production |
| Obligatory thermogenesis | Basic cellular functions | 60% |
| Exercise-associated thermogenesis (EAT) | Muscle contractions during exercise | 20% |
| Diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) | Eating | 10% |
| Adaptive thermogenesis | Changes in environmental temperature | 10% |
| Non-Shivering thermogenesis (NST) | Production of heat by brown adipose tissue (BAT) in response to cold | 10% |
Obligatory Thermogenesis
Obligatory thermogenesis is the energy expenditure required for essential bodily functions, such as respiration, circulation, digestion, and maintaining body temperature. It accounts for a significant portion of daily energy expenditure, typically around 60-70% of total energy expenditure. Obligatory thermogenesis is relatively constant and is not affected by external factors such as diet or exercise.
Exercise-associated Thermogenesis (EAT)
Exercise-associated thermogenesis (EAT) is the increase in energy expenditure during and after exercise. EAT is proportional to the intensity and duration of exercise. For example, a high-intensity workout will burn more calories than a low-intensity workout, and a longer workout will burn more calories than a shorter workout.
Diet-induced Thermogenesis (DIT)
Diet-induced thermogenesis (DIT) is the increase in energy expenditure following a meal. DIT is caused by the body’s efforts to digest, absorb, and process the nutrients in the food. DIT accounts for approximately 10% of the calories consumed in a meal. Protein has a higher thermic effect than carbohydrates or fats, meaning it burns more calories during digestion.
Adaptive Thermogenesis
Adaptive thermogenesis is the increase in energy expenditure in response to specific stimuli, such as cold exposure, dietary changes, or exercise. It serves to maintain body temperature and protect against hypothermia. Adaptive thermogenesis accounts for the remaining 30-40% of daily energy expenditure.
Non-Shivering Thermogenesis (NST)
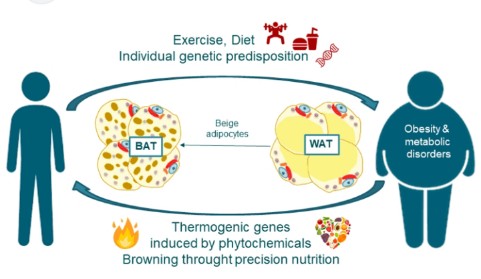
Non-shivering thermogenesis (NST) is the increase in energy expenditure in response to cold exposure. NST is mediated by the activation of brown adipose tissue (BAT) and other tissues. BAT is a specialized type of adipose tissue that is particularly adept at generating heat. It is most abundant in infants and young children, but its activity tends to decrease with age.
Top Thermogenic Foods That Help Burn Fat Quickly
Here’s a list of top thermogenic foods that may help burn fat quickly, along with potential benefits and drawbacks:
Caffeine
Caffeine is a stimulant that can increase metabolism and energy expenditure. It may also help reduce appetite and promote fat burning. However, excessive caffeine intake can lead to jitters, anxiety, and sleep disturbances.
Green Tea
Green tea contains catechins, antioxidants that may boost metabolism and enhance fat burning. It also contains L-theanine, an amino acid that may promote relaxation and reduce stress.
Coconut Oil
Coconut oil contains medium-chain triglycerides (MCTs), which are easily absorbed and metabolized by the body. MCTs may help increase energy expenditure and promote fat burning. However, coconut oil is high in saturated fat, so it should be consumed in moderation.
Proteins
Protein requires more energy to digest than carbohydrates or fats, leading to a higher thermic effect. Consuming protein-rich foods may help increase metabolism and promote fat burning.
Ginger
Ginger contains gingerols, compounds that may have anti-inflammatory and thermogenic properties. Ginger may help increase metabolism and promote fat burning.
Foods Containing Capsaicin
Capsaicin, the active ingredient in chili peppers, may increase metabolism and promote fat burning. However, it can also irritate the digestive system.
High-Fibre Foods
High-fibre foods can promote satiety and help reduce overall calorie intake. They may also help regulate blood sugar levels and promote gut health.
Yohimbine
Yohimbine is a compound found in the bark of the yohimbe tree. It may increase metabolism and promote fat burning, particularly in combination with exercise. However, it can have serious side effects, including high blood pressure, anxiety, and heart palpitations.
Thermal Stress
Thermal stress is a condition that occurs when the body is exposed to temperatures that are too high or too low. It can cause a variety of health problems, including heatstroke, hypothermia, and dehydration.
Heatstroke is a serious condition that can occur when the body temperature rises to 104 degrees Fahrenheit or higher. Symptoms of heatstroke include confusion, dizziness, headache, nausea, vomiting, and seizures. If left untreated, heatstroke can be fatal.
Hypothermia is a condition that occurs when the body temperature falls below 95 degrees Fahrenheit. Symptoms of hypothermia include shivering, fatigue, confusion, slurred speech, and loss of coordination. If left untreated, hypothermia can lead to coma and death.
Dehydration is a condition that occurs when the body loses more fluids than it takes in. Symptoms of dehydration include thirst, fatigue, dry mouth, and dizziness. If left untreated, dehydration can lead to serious health problems, including heat stroke and hypothermia.
Thermogenic Fat Burners
Thermogenic fat burners are supplements that are designed to boost metabolism and help people burn more fat. They typically work by increasing the body’s thermogenesis, which is the process of heat production. This can lead to an increase in calorie burning, even at rest.
There are a number of different types of thermogenic fat burners available, including:
Stimulants: Stimulants such as caffeine, ephedrine, and guarana can increase metabolism and energy levels.
Lipotropics: Lipotropics are substances that help the body break down and burn fat. Some common lipotropics include choline, inositol, and methionine.
Thyroid hormones: Thyroid hormones regulate metabolism. Synthetic thyroid hormones, such as liothyronine (T3) and liothyroxine (T4), are sometimes prescribed for people with hypothyroidism, a condition in which the thyroid gland does not produce enough hormones. However, they can be dangerous if taken without a prescription.
Thermogenic fat burners can be effective for some people, but they are not a magic bullet for weight loss. They should be used in conjunction with a healthy diet and exercise program.
It is important to note that the effectiveness of non-stimulant thermogenics is not as well-established as the effectiveness of stimulant thermogenics and herbal thermogenics. Some studies have shown that they can be effective for weight loss, while other studies have shown that they are not effective.
As with any supplement, it is important to talk to your doctor before taking thermogenic fat burners. They can help you determine if they are safe for you and if they are right for your individual needs.
| Some Additional Tips for Burning Fat QuicklyEat a healthy diet: Focus on eating plenty of fruits, vegetables, and whole grains. Limit your intake of processed foods, sugary drinks, and unhealthy fats.Exercise regularly: Aim for at least 30 minutes of moderate-intensity exercise most days of the week.Get enough sleep: When you don’t get enough sleep, your body produces more of the stress hormone cortisol, which can lead to fat storage. Aim for 7-8 hours of sleep each night.Reduce stress: Stress can also lead to fat storage. Find healthy ways to manage stress, such as yoga, meditation, or spending time in nature. |


 Home
Home