Frequent knee discomfort is a prevalent issue that can arise from various causes, posing challenges to mobility and daily activities. The knee joint is intricate, and a variety of factors can contribute to its deterioration and the consequent pain.
When the different components of the knee fail to function correctly, it can lead to pain, inflammation, and other associated symptoms. These problems can arise from injuries or underlying medical conditions.
The knee joint is formed by the connection of the thighbone, shinbone, and kneecap (patella), and it encompasses several crucial components such as cartilage, ligaments, menisci, and tendons.
Cartilage, a smooth substance covering the ends of the knee bones, enables seamless movement and reduces friction during bending and straightening of the leg. The menisci serve as cushions positioned between the femur and tibia, playing a vital role in shock absorption.
Ligaments provide stability to the knee by holding the bones together. They can be damaged due to overuse, such as in sports activities, or as a result of traumatic injuries. Tendons are connective tissues that attach the leg muscles to the corresponding bones, facilitating movement and control.
When all these components work harmoniously, the knee functions optimally, allowing individuals to move freely. Sadly, a majority of people are experiencing knee pain.
Table of Contents
Causes of Knee Pain
Trauma
Traumatic knee injuries can occur due to various factors, such as falling from a height, receiving a direct blow to the knee, sudden changes in direction, or repetitive movements during sports training. An orthopedist will typically evaluate the extent of the injury through comprehensive physical examination and imaging tests like X-rays, MRI scans, or CT scans, and a treatment plan may be recommended accordingly.
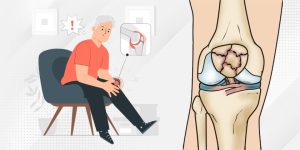
These injuries can result in:
- Dislocation of the kneecap
- Fractures in the kneecap, femur, or tibia
- Torn ligaments
- Meniscus tears
Such injuries are often attributed to several causes, including:
- Failure to warm up properly before or after exercise or engaging in excessively intense physical activity
- Participation in sports activities, particularly without using appropriate protective gear
- Involvement in road traffic accidents or experiencing falls
Accidents, falls, and strenuous physical activities frequently subject the knee to extreme stress. If the knee does not heal correctly, it can lead to chronic pain. Common issues associated with traumatic knee injuries encompass bone fractures, dislocated kneecaps, and torn ligaments.
Medical
Knee pain can arise from various medical conditions, including:
- Degenerative tissue disorders, such as osteoarthritis.
- Auto-inflammatory diseases, like rheumatoid arthritis.
- Tendinitis, which is characterized by inflammation of a tendon, resulting in pain while walking upstairs.
- Bursitis, an inflammation caused by overuse.
- Chondromalacia patella, involving damage to the cartilage beneath the kneecap.
- Gout, a form of arthritis.
- Baker’s cyst, which occurs when fluid accumulates behind the knee.
- Tumors, either benign or malignant, affecting the knee.
Gout
Gout, classified as a metabolic disorder, can lead to knee pain due to the accumulation of uric acid crystals in the joints. This accumulation often triggers painful inflammation and can also impact the knee’s range of motion.
Bacterial Infection
The sudden onset of knee pain can be attributed to bacterial infections, such as cellulitis. Cellulitis occurs when bacteria, typically present on the skin’s surface, penetrate beneath the protective layer of the skin.
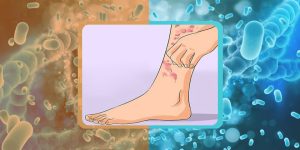
If left untreated, cellulitis around the knee can lead to joint infection, characterized by redness, swelling, pain, and stiffness.
Over time, this can progress into chronic knee pain.
Symptoms That May Indicate a Knee-Related Issue Include:
- Swelling, warmth, or redness in the knee.
- Sensations of stiffness, locking, grinding, or buckling in the knee.
- Prickling, burning, or tingling feelings in the knee.
- Frequent muscle spasms around the knee.
- Pain experienced in the calf, hip, shin, ankle, or thigh.
- Weakness or an inability to fully extend the leg.
- Popping or crackling sounds when straightening or bending the leg.
Treatment for Knee Pain
Based on the underlying cause of the issue, the doctor may suggest the following recommendations for knee pain treatment:

- Prescription of pain relief medication or other suitable drugs.
- Implementation of an exercise plan, potentially involving low-impact exercises.
- Adequate rest for the knee.
- Wearing a knee support or brace.
- Consideration of surgical intervention, if necessary.
Pain-relief medications often include anti-inflammatory drugs that effectively alleviate pain and reduce swelling.
Treatment of Knee Pain
Depending on the cause of the problem, the doctor from The Lower Limb Clinic may recommend:
- Pain relief medication or other drugs
- An exercise plan, which may include low-stress exercise
- Resting the knee
- A knee support
- Surgery
Pain-relief medications include anti-inflammatory drugs that will reduce the pain and swelling. Orthopedists usually recommend nonsteroidal anti-inflammatory drugs (NSAIDs) such as ibuprofen or naproxen to help alleviate pain and reduce inflammation in the knee joint or injury. These medications can be taken orally or applied topically as creams or gels.
In addition to medication, physical therapy strengthens the muscles surrounding the knee joint and enhances flexibility and range of motion. Physical therapists can tailor exercises to the individual’s needs and gradually progress the intensity as the knee improves.
In some cases, corticosteroid injections may be administered directly into the knee joint to provide temporary relief from pain and inflammation, particularly if other conservative measures have been unsuccessful.
If conservative treatments fail to provide relief or if there is significant damage to the knee joint, surgery may be required. Surgical options may include arthroscopic procedures to repair damaged cartilage or ligaments, partial or total knee replacement for severe osteoarthritis, or other procedures depending on the specific condition causing the knee pain.
It’s essential for individuals experiencing knee pain to consult with a healthcare professional, such as a doctor or orthopedic specialist, to receive an accurate diagnosis and appropriate treatment plan tailored to their needs.
In the Nutshell!
Knee pain can manifest due to a diverse range of factors. If an individual is dealing with persistent knee pain, it is advisable to seek medical attention.
During the medical consultation, the doctor will inquire about the symptoms and conduct a physical examination. Additionally, they may recommend imaging tests such as X-rays or MRI scans to aid in diagnosis. Once the underlying cause is determined, the doctor will discuss appropriate treatment options.
Prompt and suitable treatment can help prevent a transient or acute knee problem from progressing into a long-term or chronic condition.
Author Bio:

Dr. Prateek Kumar Gupta is a highly trained arthroscopy and sports surgeon in AOSM. He treats sports injury and other orthopedic injuries including foot, ankle, hip, and elbow with a special interest in knee and shoulder issues that hinders the patient/player’s quality of life.


 Home
Home